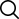Ginkgo Biloba Leaf

Also known as Ginkgo biloba, and Maidenhair Tree.
Introduction Ginkgo, the oldest living species of plant on earth, is more than 225 million years old. In this U.S. it has been one of the ten best selling herbs for more than 5 years and a standardized extract of ginkgo leaf is presently one of the most frequently used plant-based medicines in Europe. In Germany, ginkgo is also an approved therapy for the treatment of memory loss in conditions such as Alzheimer's, ringing in the ears, dizziness, and poor circulation in the lower legs resulting in pain during walking.
Constituents Gibberellin, cytokinin-like substances, ginkgolic acid, bilobol, ginnol, aspartine, calcium.
Parts Used Leaves and nuts. Leaves are considered "sweeter" and have a gentle effect and are primarily used for cerebral circulation.
Typical Preparations Teas, capsules, and extracts.
Summary The natural herb has a long history in Chinese medicine. Ginkgo nuts and ginkgo leaves are used to treat lung conditions (rather than mental conditions). They are sweet, astringent, and non-heating; they stop "leakage" of fluids into air passageways without causing heat, increased heartbeat, or excitability. Recent research into the plant has discovered a range of medicinally active compounds in the leaves and this has excited a lot of interest in the health-promoting potential of the plant. In particular, the leaves stimulate the blood circulation and have a tonic effect on the brain, reducing lethargy, improving memory, and giving an improved sense of well-being. They have also been shown to be effective in improving peripheral arterial circulation and in treating hearing disorders such as tinnitus where these result from poor circulation or damage by free radicals. The leaves contain ginkgolides, these are compounds that are unknown in any other plant species. Ginkgolides inhibit allergic responses and so are of use in treating disorders such as asthma. Eye disorders and senility have also responded to treatment. The leaves are best harvested in the late summer or early autumn just as they begin to change color. They are dried for later use.
Precautions The leaf is not recommended for persons currently taking blood thinning medications. For nuts- do not use if you have a current outbreak of poison ivy or contact dermatitis, since the increased circulation to the skin caused by the herb could spread the toxin.
PURCHASE GINKGO BILOBA LEAF EXTRACT
For educational purposes only. This information has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
This information courtesy of MOUNTAIN ROSE HERBS, with full, written permission for reuse.